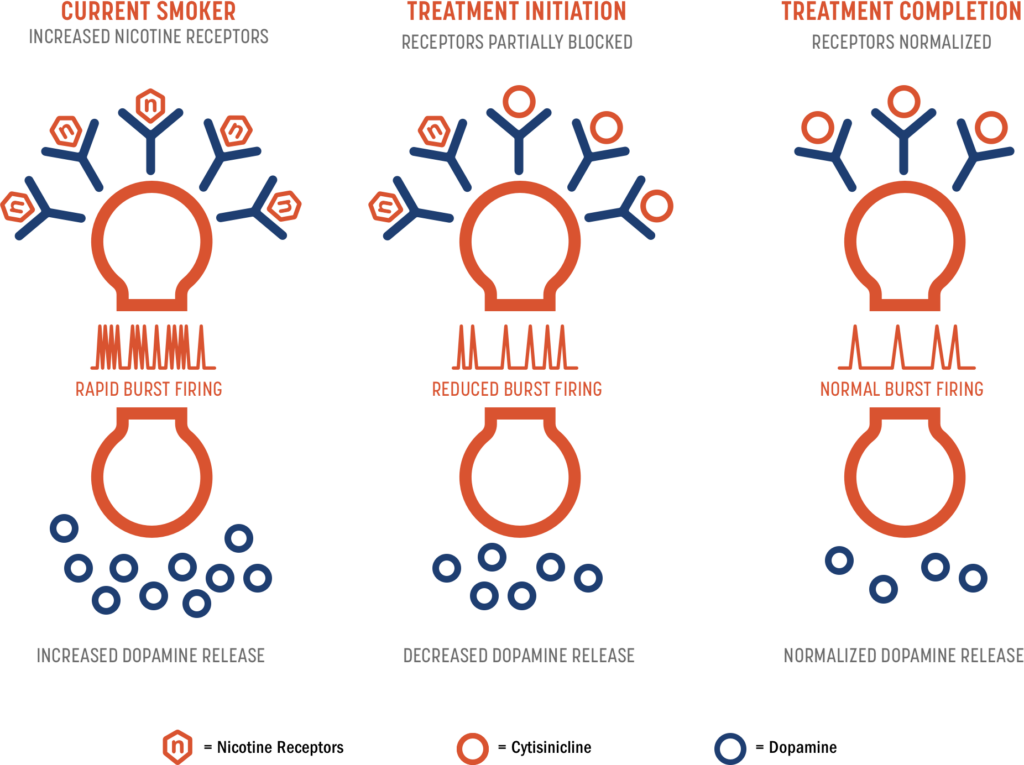
Dual-Action Mechanism
Cytisinicline is believed to reduce nicotine cravings, withdrawal symptoms, and reward and satisfaction associated with smoking and vaping by targeting nicotine receptors. When nicotine binds to this receptor, it causes dopamine to be released. Cytisinicline acts as a partial agonist, preventing nicotine from binding and releasing dopamine.